With the exponential rise in remote working, ‘bring your own device’ (BYOD) has become a mainstay of many organisations. Employees are increasingly working from their personal laptops or accessing work systems from their personal mobile phones when at home. And in some cases, ‘bring your own device’ extends to bringing personal devices into the workplace.
But with BYOD comes a new selection IT security (and potentially HR) issues. So how can an organisation approach BYOD management and best protect itself?
BYOD & cybersecurity
When employees use their own mobiles, tablets, laptops or desktops for remote working, it exposes an organisation to new security vulnerabilities. These can include new risks of malware or phishing that work firewalls or antivirus would normally have covered.
There can also be an increased risk of work data loss should a personal device connected to work emails or systems become lost or stolen (note this would also be a GDPR breach).

Lost BYOD devices represent a GDPR breach
Without oversight, there’s no guarantee that such devices even have a password attached to them. Any organisation allowing BYOD must, therefore, consider ways to mitigate the rise in security risks.
Risk Mitigation Practices
When evaluating the technical controls that can be introduced to mitigate the risks inherent with BYOD, the provision of managed work devices is usually the most effective solution.
Where a managed work device solution is not possible (due to logistical constraints, budgets etc.) the implementation of a strong BYOD management policy can be viewed as the next best option.
Establishing A BYOD Management Solution
Any BYOD management policy should seek to address the active cybersecurity threat to both employee devices and remote working infrastructure, whilst remaining flexible to evolving IT security needs within the organisation.
When seeking to mitigate the risks from BYOD, IT security measures can include utilising strong authentication approaches. This can include two- or multi-factor authentication, which add additional layers of security that significantly decrease the likelihood of unauthorised access.
Monitoring of services and data being accessed by employees working remotely is another part of a BYOD management policy. Microsoft 365 security solutions can in part support the monitoring of work account use. Outside of this, Mobile Device Management can be useful.
Security & Mobile Device Management
When introducing or updating a BYOD management policy, it is worth considering adopting Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution.
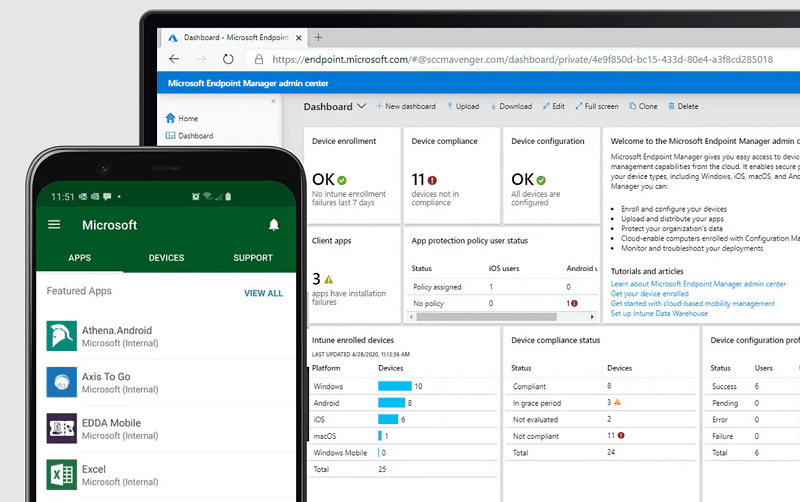
Microsoft’s MDM solution – Endpoint Manager
MDM is a way of controlling devices remotely, allowing organisations to monitor them and enforce measures as required. On managed work devices, MDM can be useful in quickly deploying work-prescribed apps, links, security software and more. It can also be used to limit functionality, such as removing the use of a phone camera, preventing work-irrelevant web browsing, or preventing the download of gaming apps.
For BYOD purposes, MDM can be used to create a partition (or bubble) within an employee’s personal device for work-related activities. This allows work emails to be kept away from personal email accounts, for example. MDM can also support the secure accessing of cloud-based applications from employee devices. It also allows organisations to apply additional security to access partitions (even if the device itself has no security), and even wipe the data held in the partition remotely if required (eg. the device is lost).
Owning ‘Bring Your Own Device’
Despite the rising challenges from BYOD management and cyber security implications, security risks can be minimised through the smart implementation of BYOD management policies. In turn, this should be supported by an appropriate update to HR policies and the provision of relevant employee training.
To discuss the IT security implications of ‘bring your own device’ or our MDM solutions, please get in touch: